Heap
Heap data structure is a specialized binary tree based
data structure. Heap is a binary tree with special characteristics. In a
heap data structure, nodes are arranged based on thier value. A heap
data structure, some time called as Binary Heap.
There are two types of heap data structures and they are as follows...

There are two types of heap data structures and they are as follows...
- Max Heap
- Min Heap
Every heap data structure has the following properties...
Property #1 (Ordering): Nodes must be arranged in a order according to values based on Max heap or Min heap.
Property #2 (Structural): All levels in a heap must full, except last level and nodes must be filled from left to right strictly.
Max Heap
Max heap data structure is a specialized full binary
tree data structure except last leaf node can be alone. In a max heap
nodes are arranged based on node value.
Max heap is defined as follows...
Max heap is defined as follows...
Max heap is a specialized full binary tree in
which every parent node contains greater or equal value than its child
nodes. And last leaf node can be alone.
Example

Above tree is satisfying both Ordering property and Structural property according to the Max Heap data structure.
Operations on Max Heap
The following operations are performed on a Max heap data structure...
- Finding Maximum
- Insertion
- Deletion
Finding Maximum Value Operation in Max Heap
Finding the node which has maximum value in a max heap
is very simple. In max heap, the root node has the maximum value than
all other nodes in the max heap. So, directly we can display root node
value as maximum value in max heap.
Insertion Operation in Max Heap
Insertion Operation in max heap is performed as follows...
- Step 1: Insert the newNode as last leaf from left to right.
- Step 2: Compare newNode value with its Parent node.
- Step 3: If newNode value is greater than its parent, then swap both of them.
- Step 4: Repeat step 2 and step 3 until newNode value is less than its parent nede (or) newNode reached to root.
Example
Consider the above max heap. Insert a new node with value 85.
Consider the above max heap. Insert a new node with value 85.
- Step 1: Insert the newNode with value 85 as last leaf from left to right. That means newNode is added as a right child of node with value 75. After adding max heap is as follows...
- Step 2: Compare newNode value (85) with its Parent node value (75). That means 85 > 75
- Step 3: Here newNode value (85) is greater than its parent value (75), then swap both of them. After wsapping, max heap is as follows...
- Step 4: Now, again compare newNode value (85) with its parent nede value (89).




Here, newNode value (85) is smaller than its parent
node value (89). So, we stop insertion process. Finally, max heap after
insetion of a new node with value 85 is as follows...

Deletion Operation in Max Heap
In a max heap, deleting last node is very simple as it is not disturbing max heap properties.
Deleting root node from a max heap is title difficult as it disturbing the max heap properties. We use the following steps to delete root node from a max heap...
Deleting root node from a max heap is title difficult as it disturbing the max heap properties. We use the following steps to delete root node from a max heap...
- Step 1: Swap the root node with last node in max heap
- Step 2: Delete last node.
- Step 3: Now, compare root value with its left child value.
- Step 4: If root value is smaller than its left child, then compare left child with its right sibling. Else goto Step 6
- Step 5: If left child value is larger than its right sibling, then swap root with left child. otherwise swap root with its right child.
- Step 6: If root value is larger than its left child, then compare root value with its right child value.
- Step 7: If root value is smaller than its right child, then swap root with rith child. otherwise stop the process.
- Step 8: Repeat the same until root node is fixed at its exact position.
Example
Consider the above max heap. Delete root node (90) from the max heap.
Consider the above max heap. Delete root node (90) from the max heap.
- Step 1: Swap the root node (90) with last node 75 in max heap After swapping max heap is as follows...
- Step 2: Delete last node. Here node with value 90. After deleting node with value 90 from heap, max heap is as follows...
- Step 3: Compare root node (75) with its left child (89).
- Step 4: Here, left child value (89) is larger than its right sibling (70), So, swap root (75) with left child (89).
- Step 5: Now, again compare 75 with its left child (36).
- Step 6: Here, node with value 75 is smaller than its right child (85). So, we swap both of them. After swapping max heap is as follows...
- Step 7: Now, compare node with value 75 with its left child (15).



Here, root value (75) is smaller than its left child value (89). So, compare left child (89) with its right sibling (70).



Here, node with value 75 is larger than its left child. So, we compare node with value 75 is compared with its right child 85.



Here, node with value 75 is larger than its left child (15) and it does not have right child. So we stop the process.
Finally, max heap after deleting root node (90) is as follows...
Finally, max heap after deleting root node (90) is as follows...

Red Black Tree
Red Black Tree is a Binary Search Tree in which every node is colored eigther RED or BLACK.
In a Red Black Tree the color of a node is decided based
on the Red Black Tree properties. Every Red Black Tree has the
following properties.
Properties of Red Black Tree
- Property #1: Red - Black Tree must be a Binary Search Tree.
- Property #2: The ROOT node must colored BLACK.
- Property #3: The children of Red colored node must colored BLACK. (There should not be two consecutive RED nodes).
- Property #4: In all the paths of the tree there must be same number of BLACK colored nodes.
- Property #5: Every new node must inserted with RED color.
- Property #6: Every leaf (e.i. NULL node) must colored BLACK.
Example
THe following is a Red Black Tree which created by inserting numbers from 1 to 9.

The above tree is a Red Black tree and every node is satisfying all the properties of Red Black Tree.
Insertion into RED BLACK Tree:
In a Red Black Tree, every new node must be inserted with color RED. The insertion operation in Red Black Tree
is similar to insertion operation in Binary Search Tree. But it is inserted with a color property. After every
insertion operation, we need to check all the properties of Red Black Tree. If all the properties are satisfied
then we go to next operation otherwise we need to perform following operation to make it Red Black Tree.
- 1. Recolor
- 3. Rotation followed by Recolor
The insertion operation in Red Black tree is performed using following steps...
- Step 1: Check whether tree is Empty.
- Step 2: If tree is Empty then insert the newNode as Root node with color Black and exit from the operation.
- step 3: If tree is not Empty then insert the newNode as a leaf node with Red color.
- Step 4: If the parent of newNode is Black then exit from the operation.
- Step 5: If the parent of newNode is Red then check the color of parent node's sibling of newNode.
- Step 6: If it is Black or NULL node then make a suitable Rotation and Recolor it.
- Step 7: If it is Red colored node then perform Recolor and Recheck it. Repeat the same until tree becomes Red Black Tree.
Example

Deletion Operation in Red Black Tree
In a Red Black Tree, the deletion operation is similar
to deletion operation in BST. But after every deletion operation we need
to check with the Red Black Tree properties. If any of the property is
voilated then make suitable operation like Recolor or Rotaton &
Recolor.
B - Trees
In a binary search tree, AVL Tree, Red-Black tree etc.,
every node can have only one value (key) and maximum of two children but
there is another type of search tree called B-Tree in which a node can
store more than one value (key) and it can have more than two children.
B-Tree was developed in the year of 1972 by Bayer and McCreight with the name Height Balanced m-way Search Tree. Later it was named as B-Tree.
B-Tree can be defined as follows...


B-Tree can be defined as follows...
B-Tree is a self-balanced search tree with multiple keys in every node and more than two children for every node.
Here, number of keys in a node and number of children for a node is depend on the order of the B-Tree. Every B-Tree has order.
B-Tree of Order m has the following properties...
B-Tree of Order m has the following properties...
- Property #1 - All the leaf nodes must be at same level.
- Property #2 - All nodes except root must have at least [m/2]-1 keys and maximum of m-1 keys.
- Property #3 - All non leaf nodes except root (i.e. all internal nodes) must have at least m/2 children.
- Property #4 - If the root node is a non leaf node, then it must have at least 2 children.
- Property #5 - A non leaf node with n-1 keys must have n number of children.
- Property #6 - All the key values within a node must be in Ascending Order.
For example, B-Tree of Order 4 contains maximum 3 key values in a node and maximum 4 children for a node.
Example

Operations on a B-Tree
The following operations are performed on a B-Tree...
- Search
- Insertion
- Deletion
Search Operation in B-Tree
In a B-Ttree, the search operation is similar to that of
Binary Search Tree. In a Binary search tree, the search process starts
from the root node and every time we make a 2-way decision (we go to
either left subtree or right subtree). In B-Tree also search process
starts from the root node but every time we make n-way decision where n
is the total number of children that node has. In a B-Ttree, the search
operation is performed with O(log n) time complexity. The search operation is performed as follows...
- Step 1: Read the search element from the user
- Step 2: Compare, the search element with first key value of root node in the tree.
- Step 3: If both are matching, then display "Given node found!!!" and terminate the function
- Step 4: If both are not matching, then check whether search element is smaller or larger than that key value.
- Step 5: If search element is smaller, then continue the search process in left subtree.
- Step 6: If search element is larger, then compare with next key value in the same node and repeate step 3, 4, 5 and 6 until we found exact match or comparision completed with last key value in a leaf node.
- Step 7: If we completed with last key value in a leaf node, then display "Element is not found" and terminate the function.
Insertion Operation in B-Tree
In a B-Tree, the new element must be added only at leaf
node. That means, always the new keyValue is attached to leaf node only.
The insertion operation is performed as follows...
- Step 1: Check whether tree is Empty.
- Step 2: If tree is Empty, then create a new node with new key value and insert into the tree as a root node.
- Step 3: If tree is Not Empty, then find a leaf node to which the new key value cab be added using Binary Search Tree logic.
- Step 4: If that leaf node has an empty position, then add the new key value to that leaf node by maintaining ascending order of key value within the node.
- Step 5: If that leaf node is already full, then split that leaf node by sending middle value to its parent node. Repeat tha same until sending value is fixed into a node.
- Step 6: If the spilting is occuring to the root node, then the middle value becomes new root node for the tree and the height of the tree is increased by one.
Example
Construct a B-Tree of Order 3 by inserting numbers from 1 to 10.

Splay Tree
Splay tree is another varient of binary search tree. In a
splay tree, the recently accessed element is placed at the root of the
tree. A splay tree is defined as follows...






Every Splay tree must be a binary search tree but it is need not to be balanced tree.
Splay Tree is a self - adjusted Binary Search Tree
in which every operation on an element rearrange the tree so that the
element is placed at the root position of the tree.
In a splay tree, every operation is performed at root of
the tree. All the operations on a splay tree are involved with a common
operation called "Splaying".
Splaying an element is the process of bringing it to the root position by performing suitable rotation operations.
In a splay tree, splaying an element rearrange all the
elements in the tree so that splayed element is placed at root of the
tree.
With the help of splaying an element we can bring most frequently used element closer to the root of the tree so that any operation on those element performed quickly. That means the splaying operation automatically brings more frequently used elements closer to the root of the tree.
Every operation on a splay tree performs the splaying operation. For example, the insertion operation first inserts the new element as it inserted into the binary search tree, after insertion the newly inserted element is splayed so that it is placed at root of the tree. The search operation in a splay tree is search the element using binary search process then splay the searched element so that it placed at the root of the tree.
In a splay tree, to splay any element we use the following rotation operations...
With the help of splaying an element we can bring most frequently used element closer to the root of the tree so that any operation on those element performed quickly. That means the splaying operation automatically brings more frequently used elements closer to the root of the tree.
Every operation on a splay tree performs the splaying operation. For example, the insertion operation first inserts the new element as it inserted into the binary search tree, after insertion the newly inserted element is splayed so that it is placed at root of the tree. The search operation in a splay tree is search the element using binary search process then splay the searched element so that it placed at the root of the tree.
In a splay tree, to splay any element we use the following rotation operations...
Rotations in Splay Tree
- 1. Zig Rotation
- 2. Zag Rotation
- 3. Zig - Zig Rotation
- 4. Zag - Zag Rotation
- 5. Zig - Zag Rotation
- 6. Zag - Zig Rotation
Example
Zig Rotation
The Zig Rotation in a splay tree is
similar to the single right rotation in AVL Tree rotations. In zig
rotation every node moves one position to thr righ from its current
position. Consider the following example...

Zag Rotation
The Zag Rotation in a splay tree is
similar to the single left rotation in AVL Tree rotations. In zag
rotation every node moves one position to the left from its current
position. Consider the following example...

Zig-Zig Rotation
The Zig-Zig Rotation in a splay tree is
a double zig rotation. In zig-zig rotation every node moves two
position to the right from its current position. Consider the following
example...

Zag-Zag Rotation
The Zag-Zag Rotation in a splay tree is
a double zag rotation. In zag-zag rotation every node moves two
position to the left from its current position. Consider the following
example...

Zig-Zag Rotation
The Zig-Zag Rotation in a splay tree is
a sequence of zig rotation followed by zag rotation. In zig-zag
rotation every node moves one position to the right followed by one
position to the left from its current position. Consider the following
example...

Zag-Zig Rotation
The Zag-Zig Rotation in a splay tree is
a sequence of zag rotation followed by zig rotation. In zag-zig
rotation every node moves one position to the left followed by one
position to the right from its current position. Consider the following
example...

Insertion Operation in Splay Tree
The insertion operation in Splay tree is performed using following steps...
- Step 1: Check whether tree is Empty.
- Step 2: If tree is Empty then insert the newNode as Root node and exit from the operation.
- step 3: If tree is not Empty then insert the newNode as a leaf node using Binary Search tree insertion logic.
- Step 4: After insertion, Splay the newNode
Deletion Operation in Splay Tree
In a Splay Tree, the deletion operation is similar to
deletion operation in Binary Search Tree. But before deleting the
element first we need to splay that node then delete it from the root position then join the remaining tree.
AVL Tree
AVL tree is a self balanced binary search tree. That
means, an AVL tree is also a binary search tree but it is a balanced
tree. A binary tree is said to be balanced, if the difference between
the hieghts of left and right subtrees of every node in the tree is
either -1, 0 or +1. In other words, a binary tree is said to be balanced
if for every node, height of its children differ by at most one. In an
AVL tree, every node maintains a extra information known as balance factor. The AVL tree was introduced in the year of 1962 by G.M. Adelson-Velsky and E.M. Landis.
An AVL tree is defined as follows...

Every AVL Tree is a binary search tree but all the Binary Search Trees need not to be AVL trees.






An AVL tree is defined as follows...
An AVL tree is a balanced binary search tree. In an AVL tree, balance factor of every node is either -1, 0 or +1.
Balance factor of a node is the difference between the
heights of left and right subtrees of that node. The balance factor of a
node is calculated either height of left subtree - height of right subtree (OR) height of right subtree - height of left subtree. In the following explanation, we are calculating as follows...
Balance factor = heightOfLeftSubtree - heightOfRightSubtree
Example

The above tree is a binary search tree and every node is
satisfying balance factor condition. So this tree is said to be an AVL
tree.
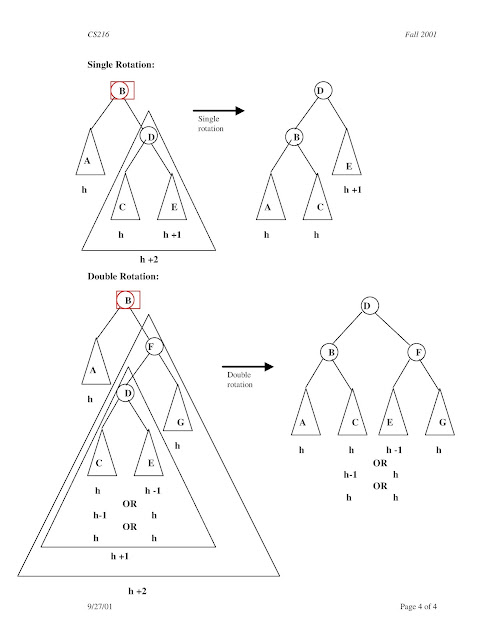
AVL Tree Rotations
In AVL tree, after performing every operation like insertion and deletion we need to check the balance factor
of every node in the tree. If every node satisfies the balance factor
condition then we conclude the operation otherwise we must make it
balanced. We use rotation operations to make the tree balanced whenever the tree is becoming imbalanced due to any operation.
Rotation operations are used to make a tree balanced.
Rotation operations are used to make a tree balanced.
Rotation is the process of moving the nodes to either left or right to make tree balanced.
There are four rotations and they are classified into two types.

Single Left Rotation (LL Rotation)
In LL Rotation every node moves one position to left
from the current position. To understand LL Rotation, let us consider
following insertion operations into an AVL Tree...

Single Right Rotation (RR Rotation)
In RR Rotation every node moves one position to right
from the current position. To understand RR Rotation, let us consider
following insertion operations into an AVL Tree...

Left Right Rotation (LR Rotation)
The LR Rotation is combination of single left rotation
followed by single right rotation. In LR Roration, first every node
moves one position to left then one position to right from the current
position. To understand LR Rotation, let us consider following insertion
operations into an AVL Tree...

Right Left Rotation (RL Rotation)
The RL Rotation is combination of single right rotation
followed by single left rotation. In RL Roration, first every node
moves one position to right then one position to left from the current
position. To understand RL Rotation, let us consider following insertion
operations into an AVL Tree...

Operations on an AVL Tree
The following operations are performed on an AVL tree...
- Search
- Insertion
- Deletion
Search Operation in AVL Tree
In an AVL tree, the search operation is performed with O(log n)
time complexity. The search operation is performed similar to Binary
search tree search operation. We use the following steps to search an
element in AVL tree...
- Step 1: Read the search element from the user
- Step 2: Compare, the search element with the value of root node in the tree.
- Step 3: If both are matching, then display "Given node found!!!" and terminate the function
- Step 4: If both are not matching, then check whether search element is smaller or larger than that node value.
- Step 5: If search element is smaller, then continue the search process in left subtree.
- Step 6: If search element is larger, then continue the search process in right subtree.
- Step 7: Repeat the same until we found exact element or we completed with a leaf node
- Step 8: If we reach to the node with search value, then display "Element is found" and terminate the function.
- Step 9: If we reach to a leaf node and it is also not matching, then display "Element not found" and terminate the function.
Insertion Operation in AVL Tree
In an AVL tree, the insertion operation is performed with O(log n) time complexity. In AVL Tree, new node is always inserted as a leaf node. The insertion operation is performed as follows...
- Step 1: Insert the new element into the tree using Binary Search Tree insertion logic.
- Step 2: After insertion, check the Balance Factor of every node.
- Step 3: If the Balance Factor of every node is 0 or 1 or -1 then go for next operation.
- Step 4: If the Balance Factor of any node is other than 0 or 1 or -1 then tree is said to be imbalanced. Then perform the suitable Rotation to make it balanced. And go for next operation.
Example: Construct an AVL Tree by inserting numbers from 1 to 8.

Deletion Operation in AVL Tree
In an AVL Tree, the deletion operation is similar to
deletion operation in BST. But after every deletion operation we need to
check with the Balance Factor condition. If the tree is balanced after
deletion then go for next operation otherwise perform the suitable
rotation to make the tree Balanced.
Example: Construct an AVL Tree
Binary Search Tree
In a binary tree, every node can have maximum of two
children but there is no order of nodes based on their values. In binary
tree, the elements are arranged as they arrive to the tree, from top to
bottom and left to right.
A binary tree has the following time complexities.


Every Binary Search Tree is a binary tree but all the Binary Trees need not to be binary search trees.

A binary tree has the following time complexities.
- Search Operation - O(n)
- Insertion Operation - O(1)
- Deletion Operation - O(n)
To enhance the performance of binary tree, we use special type of binary tree known as Binary Search Tree. Binary search tree mainly focus on the search operation in binary tree. Binary search tree can be defined as follows...
Binary Search Tree is a binary tree in which every
node contains only smaller values in its left subtree and only larger
values in its right subtree.
In a binary search tree, all the nodes in left subtree
of any node contains smaller values and all the nodes in right subtree
of that contains larger values as shown in following figure...

Example
The following tree is a Binary Search Tree. In this
tree, left subtree of every node contains nodes with smaller values and
right subtree of every node contains larger values.

Operations on a Binary Search Tree
The following operations are performed on a binary earch tree...
- Search
- Insertion
- Deletion
Search Operation in BST
In a binary search tree, the search operation is performed with O(log n) time complexity. The search operation is performed as follows...
- Step 1: Read the search element from the user
- Step 2: Compare, the search element with the value of root node in the tree.
- Step 3: If both are matching, then display "Given node found!!!" and terminate the function
- Step 4: If both are not matching, then check whether search element is smaller or larger than that node value.
- Step 5: If search element is smaller, then continue the search process in left subtree.
- Step 6: If search element is larger, then continue the search process in right subtree.
- Step 7: Repeat the same until we found exact element or we completed with a leaf node
- Step 8: If we reach to the node with search value, then display "Element is found" and terminate the function.
- Step 9: If we reach to a leaf node and it is also not matching, then display "Element not found" and terminate the function.
Insertion Operation in BST
In a binary search tree, the insertion operation is performed with O(log n)
time complexity. In binary search tree, new node is always inserted as a
leaf node. The insertion operation is performed as follows...
- Step 1: Create a newNode with given value and set its left and right to NULL.
- Step 2: Check whether tree is Empty.
- Step 3: If the tree is Empty, then set set root to newNode.
- Step 4: If the tree is Not Empty, then check whether value of newNode is smaller or larger than the node (here it is root node).
- Step 5: If newNode is smaller than or equal to the node, then move to its left child. If newNode is larger than the node, then move to its right child.
- Step 6: Repeat the above step until we reach to a leaf node (e.i., reach to NULL).
- Step 7: After reaching a leaf node, then isert the newNode as left child if newNode is smaller or equal to that leaf else insert it as right child.
Deletion Operation in BST
In a binary search tree, the deletion operation is performed with O(log n) time complexity. Deleting a node from Binary search tree has follwing three cases...
- Case 1: Deleting a Leaf node (A node with no children)
- Case 2: Deleting a node with one child
- Case 3: Deleting a node with two children
Case 1: Deleting a leaf node
We use the following steps to delete a leaf node from BST...
- Step 1: Find the node to be deleted using search operation
- Step 2: Delete the node using free function (If it is a leaf) and terminate the function.
Case 2: Deleting a node with one child
We use the following steps to delete a node with one child from BST...
- Step 1: Find the node to be deleted using search operation
- Step 2: If it has only one child, then create a link between its parent and child nodes.
- Step 3: Delete the node using free function and terminate the function.
Case 3: Deleting a node with two children
We use the following steps to delete a node with two children from BST...
- Step 1: Find the node to be deleted using search operation
- Step 2: If it has two children, then find the largest node in its left subtree (OR) the smallest node in its right subtree.
- Step 3: Swap both deleting node and node which found in above step.
- Step 4: Then, check whether deleting node came to case 1 or case 2 else goto steps 2
- Step 5: If it comes to case 1, then delete using case 1 logic.
- Step 6: If it comes to case 2, then delete using case 2 logic.
- Step 7: Repeat the same process until node is deleted from the tree.
Example
Construct a Binary Search Tree by inserting the following sequence of numbers...
10,12,5,4,20,8,7,15 and 13
Above elements are inserted into a Binary Search Tree as follows...

Expression Tree Construction
A binary expression tree is a specific kind of a binary tree used to represent expressions
The leaves of a binary expression tree are operands, such as constants or variable names, and the other nodes contain operators. These particular trees happen to be binary, because all of the operations are binary, and although this is the simplest case, it is possible for nodes to have more than two children. It is also possible for a node to have only one child, as is the case with the unary minus operator
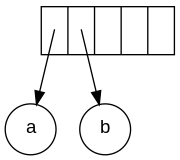
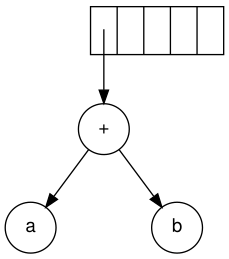
The next symbol is a '+'. It pops the two pointers to the trees, a
new tree is formed, and a pointer to it is pushed onto to the stack.
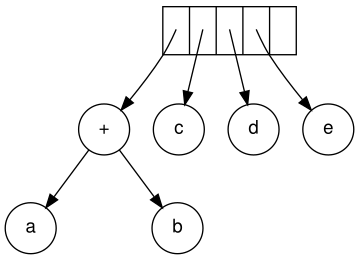
Next, c, d, and e are read. A one-node tree is created for each and a
pointer to the corresponding tree is pushed onto the stack.
Continuing, a '+' is read, and it merges the last two trees.
Now, a '*' is read. The last two tree pointers are popped and a new tree is formed with a '*' as the root.
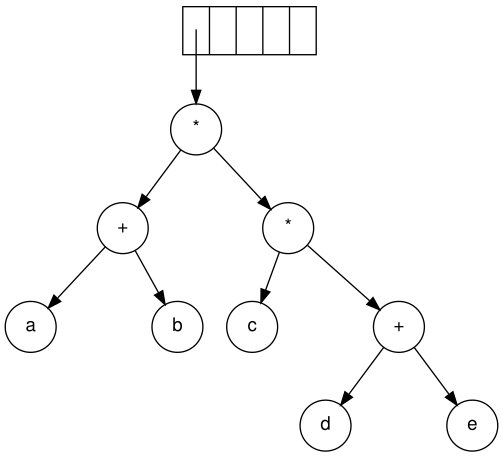
Finally, the last symbol is read. The two trees are merged and a pointer to the final tree remains on the stack.[5]
Steps to construct an expression tree a b + c d e + * *
The leaves of a binary expression tree are operands, such as constants or variable names, and the other nodes contain operators. These particular trees happen to be binary, because all of the operations are binary, and although this is the simplest case, it is possible for nodes to have more than two children. It is also possible for a node to have only one child, as is the case with the unary minus operator
Construction of an expression tree
The evaluation of the tree takes place by reading the postfix expression
one symbol at a time. If the symbol is an operand, one-node tree is
created and a pointer is pushed onto a stack. If the symbol is an operator, the pointers are popped to two trees T1 and T2 from the stack and a new tree whose root is the operator and whose left and right children point to T2 and T1 respectively is formed . A pointer to this new tree is then pushed to the Stack
Example
The input is: a b + c d e + * * Since the first two symbols are operands, one-node trees are created and pointers are pushed to them onto a stack. For convenience the stack will grow from left to right.
Stack growing from left to right
Formation of a new tree
Creating a one-node tree
Merging two trees
Forming a new tree with a root
Steps to construct an expression tree a b + c d e + * *
Postfix Expression Evaluation
A postfix expression is a collection of operators and
operands in which the operator is placed after the operands. That means,
in a postfix expression the operator follows the operands.
Postfix Expression has following general structure...
Postfix Expression has following general structure...
Operand1 Operand2 Operator
Example

Postfix Expression Evaluation using Stack Data Structure
A postfix expression can be evaluated using the Stack
data structure. To evaluate a postfix expression using Stack data
structure we can use the following steps...
Example
Consider the following Expression...

Expressions
What is an Expression?
In any programming language, if we want to perform any
calculation or to frame a condition etc., we use a set of symbols to
perform the task. These set of symbols makes an expression.
An expression can be defined as follows...
An expression can be defined as follows...
An expression is a collection of operators and operands that represents a specific value.
In above definition, operator is a symbol which performs a particular task like arithmetic operation or logical operation or conditional operation etc.,
Operands are the values on which the operators can perform the task. Here operand can be a direct value or variable or address of memory location.
Operands are the values on which the operators can perform the task. Here operand can be a direct value or variable or address of memory location.
Expression Types
Based on the operator position, expressions are divided into THREE types. They are as follows...
Infix Expression
In infix expression, operator is used in between operands.
The general structure of an Infix expression is as follows...
The general structure of an Infix expression is as follows...
Operand1 Operator Operand2
Example

Postfix Expression
In postfix expression, operator is used after operands. We can say that "Operator follows the Operands".
The general structure of Postfix expression is as follows...
The general structure of Postfix expression is as follows...
Operand1 Operand2 Operator
Example

Prefix Expression
In prefix expression, operator is used before operands. We can say that "Operands follows the Operator".
The general structure of Prefix expression is as follows...
The general structure of Prefix expression is as follows...
Operator Operand1 Operand2
Example

Any expression can be represented using the above three
different types of expressions. And we can convert an expression from
one form to another form like Infix to Postfix, Infix to Prefix, Prefix to Postfix and vice versa.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)