AVL tree is a self balanced binary search tree. That
means, an AVL tree is also a binary search tree but it is a balanced
tree. A binary tree is said to be balanced, if the difference between
the hieghts of left and right subtrees of every node in the tree is
either -1, 0 or +1. In other words, a binary tree is said to be balanced
if for every node, height of its children differ by at most one. In an
AVL tree, every node maintains a extra information known as balance factor. The AVL tree was introduced in the year of 1962 by G.M. Adelson-Velsky and E.M. Landis.
An AVL tree is defined as follows...

Every AVL Tree is a binary search tree but all the Binary Search Trees need not to be AVL trees.






An AVL tree is defined as follows...
An AVL tree is a balanced binary search tree. In an AVL tree, balance factor of every node is either -1, 0 or +1.
Balance factor of a node is the difference between the
heights of left and right subtrees of that node. The balance factor of a
node is calculated either height of left subtree - height of right subtree (OR) height of right subtree - height of left subtree. In the following explanation, we are calculating as follows...
Balance factor = heightOfLeftSubtree - heightOfRightSubtree
Example

The above tree is a binary search tree and every node is
satisfying balance factor condition. So this tree is said to be an AVL
tree.
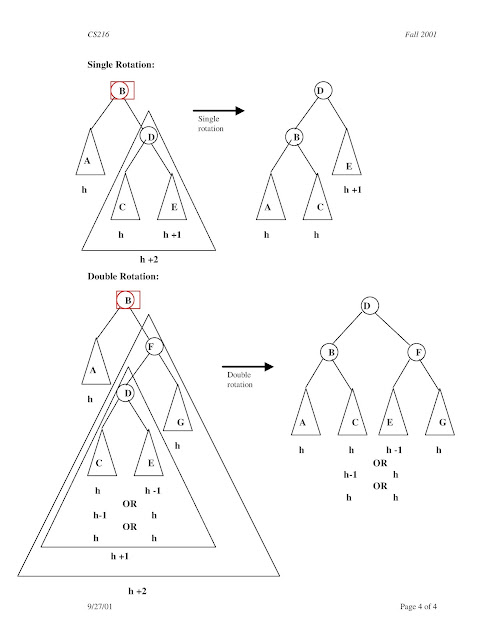
AVL Tree Rotations
In AVL tree, after performing every operation like insertion and deletion we need to check the balance factor
of every node in the tree. If every node satisfies the balance factor
condition then we conclude the operation otherwise we must make it
balanced. We use rotation operations to make the tree balanced whenever the tree is becoming imbalanced due to any operation.
Rotation operations are used to make a tree balanced.
Rotation operations are used to make a tree balanced.
Rotation is the process of moving the nodes to either left or right to make tree balanced.
There are four rotations and they are classified into two types.

Single Left Rotation (LL Rotation)
In LL Rotation every node moves one position to left
from the current position. To understand LL Rotation, let us consider
following insertion operations into an AVL Tree...

Single Right Rotation (RR Rotation)
In RR Rotation every node moves one position to right
from the current position. To understand RR Rotation, let us consider
following insertion operations into an AVL Tree...

Left Right Rotation (LR Rotation)
The LR Rotation is combination of single left rotation
followed by single right rotation. In LR Roration, first every node
moves one position to left then one position to right from the current
position. To understand LR Rotation, let us consider following insertion
operations into an AVL Tree...

Right Left Rotation (RL Rotation)
The RL Rotation is combination of single right rotation
followed by single left rotation. In RL Roration, first every node
moves one position to right then one position to left from the current
position. To understand RL Rotation, let us consider following insertion
operations into an AVL Tree...

Operations on an AVL Tree
The following operations are performed on an AVL tree...
- Search
- Insertion
- Deletion
Search Operation in AVL Tree
In an AVL tree, the search operation is performed with O(log n)
time complexity. The search operation is performed similar to Binary
search tree search operation. We use the following steps to search an
element in AVL tree...
- Step 1: Read the search element from the user
- Step 2: Compare, the search element with the value of root node in the tree.
- Step 3: If both are matching, then display "Given node found!!!" and terminate the function
- Step 4: If both are not matching, then check whether search element is smaller or larger than that node value.
- Step 5: If search element is smaller, then continue the search process in left subtree.
- Step 6: If search element is larger, then continue the search process in right subtree.
- Step 7: Repeat the same until we found exact element or we completed with a leaf node
- Step 8: If we reach to the node with search value, then display "Element is found" and terminate the function.
- Step 9: If we reach to a leaf node and it is also not matching, then display "Element not found" and terminate the function.
Insertion Operation in AVL Tree
In an AVL tree, the insertion operation is performed with O(log n) time complexity. In AVL Tree, new node is always inserted as a leaf node. The insertion operation is performed as follows...
- Step 1: Insert the new element into the tree using Binary Search Tree insertion logic.
- Step 2: After insertion, check the Balance Factor of every node.
- Step 3: If the Balance Factor of every node is 0 or 1 or -1 then go for next operation.
- Step 4: If the Balance Factor of any node is other than 0 or 1 or -1 then tree is said to be imbalanced. Then perform the suitable Rotation to make it balanced. And go for next operation.
Example: Construct an AVL Tree by inserting numbers from 1 to 8.

Deletion Operation in AVL Tree
In an AVL Tree, the deletion operation is similar to
deletion operation in BST. But after every deletion operation we need to
check with the Balance Factor condition. If the tree is balanced after
deletion then go for next operation otherwise perform the suitable
rotation to make the tree Balanced.